
The electrons are then part of both atoms and both shells are filled. Valence electrons are shared when an atom needs electrons to complete its outer shell and can share those electrons with its neighbor. Covalent BondĪ covalent bond is a chemical bond formed by shared electrons. They also tend to be soluble in water the stronger the cohesive forces, the lower the solubility. The higher the charges the stronger the cohesive forces and the higher the melting point. Ionic compounds generally have a high melting point, depending on the charge of the ions they consist of. Ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten or in solution, typically as a solid. These ions are then attracted to each other in a 1:1 ratio to form sodium chloride (NaCl). After such a transfer, the chlorine ion acquires a net negative charge, an electron configuration identical to that of argon it is also larger than the chlorine atom.
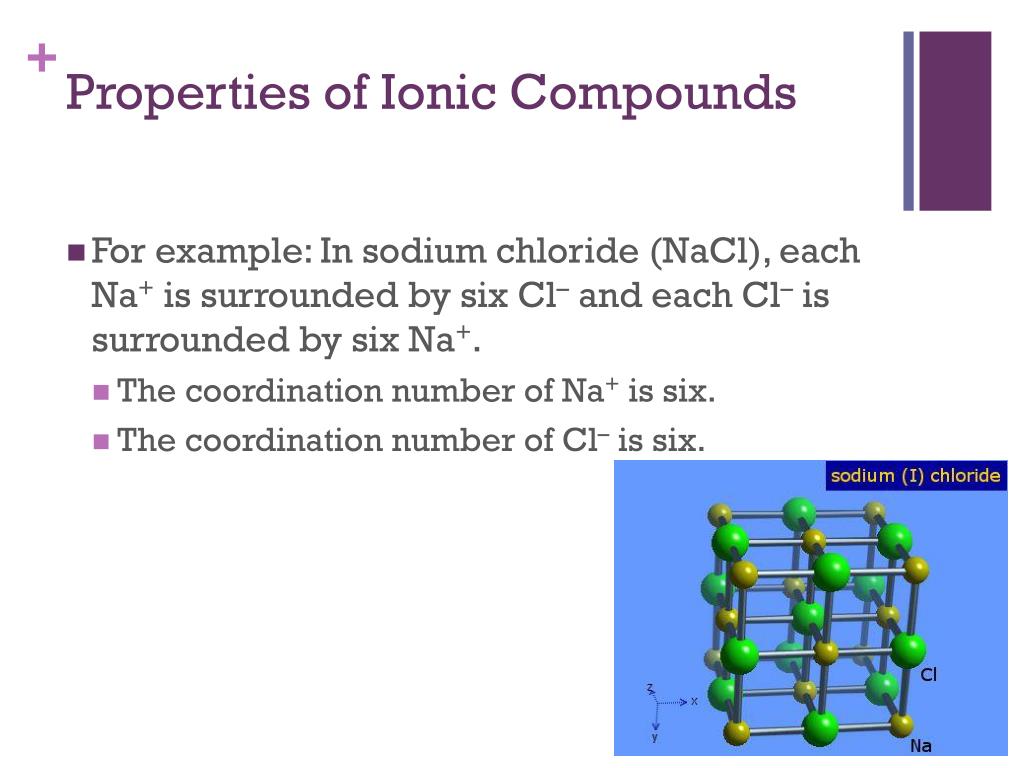
A sodium atom can assume the electron structure of neon by a transfer of its one valence 3s electron to a chlorine atom. Sodium chloride (NaCl) is the classic ionic material. For example, common table salt is sodium chloride. In the process, all the atoms acquire stable or inert gas configurations (i.e., completely filled orbital shells) and, in addition, an electrical charge – that is, they become ions. Ionic bonding leads to separate positive and negative ions. There is no precise value that distinguishes ionic from covalent bonding, but an electronegativity difference of over 1.7 is likely to be ionic while a difference of less than 1.7 is likely to be covalent. An ionic bond is always found in compounds composed of both metallic and nonmetallic elements. elements situated at the horizontal extremities of the periodic table). This type of chemical bond is typical between elements with a large electronegativity difference (i.e.
#CL ION BONDING PROPERTIES FREE#
Instead, many electrons (roughly one for each atom) are more or less free to move throughout the metal, so that each electron can interact with many of the fixed atoms.Īn ionic bond is a chemical bond, in which one or more electrons are wholly transferred from an atom of one element to the atom of the other, and the elements are held together by the force of attraction due to the opposite polarity of the charge. A metallic bond is a chemical bond, in which the atoms do not share or exchange electrons to bond together.

A covalent bond is a chemical bond formed by shared electrons. This type of chemical bond is typical between elements with a large electronegativity difference. An ionic bond is a chemical bond, in which one or more electrons are wholly transferred from an atom of one element to the atom of the other, and the elements are held together by the force of attraction due to the opposite polarity of the charge.

Therefore, the electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. The bond may result from the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds.

The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably there are “primary bonds” or “strong bonds” such as ionic, covalent and metallic bonds, and “weak bonds” or “secondary bonds” such as dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Ī chemical bond is a lasting attraction between these atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds. Three different types of primary or chemical bond are found in solids.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
